Fast and accurate
Highly adaptable
Comprehensive
Widely available
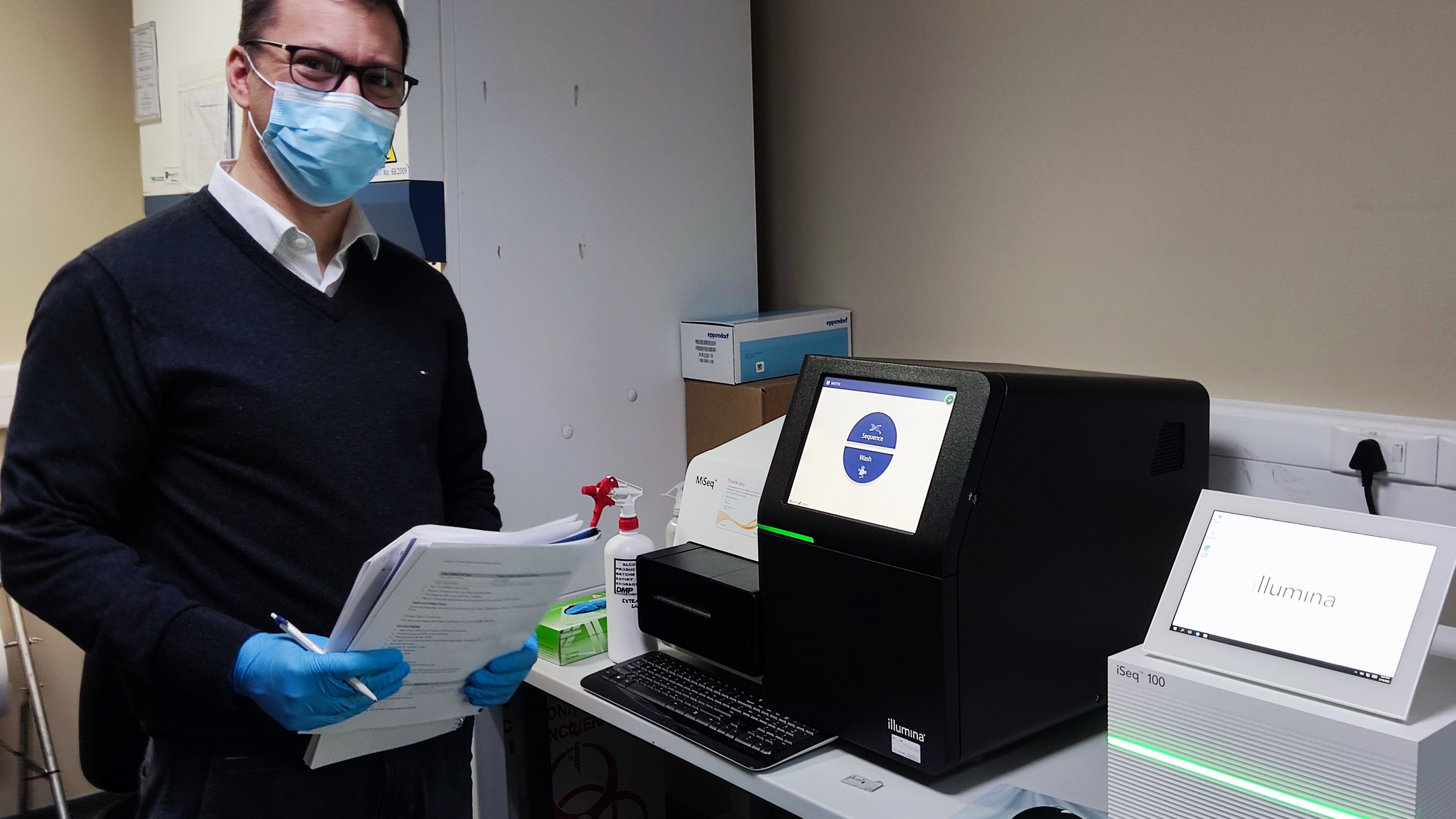
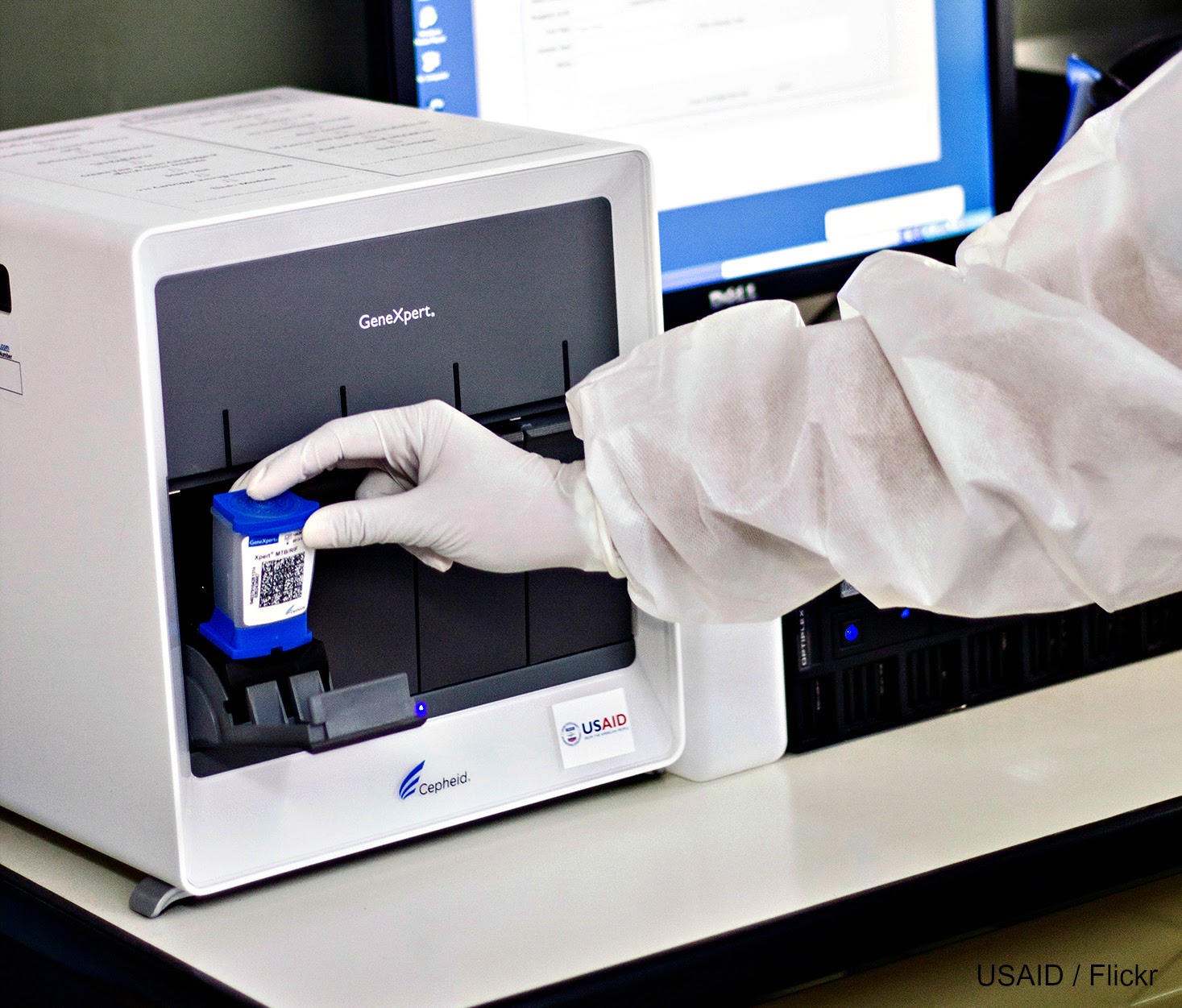
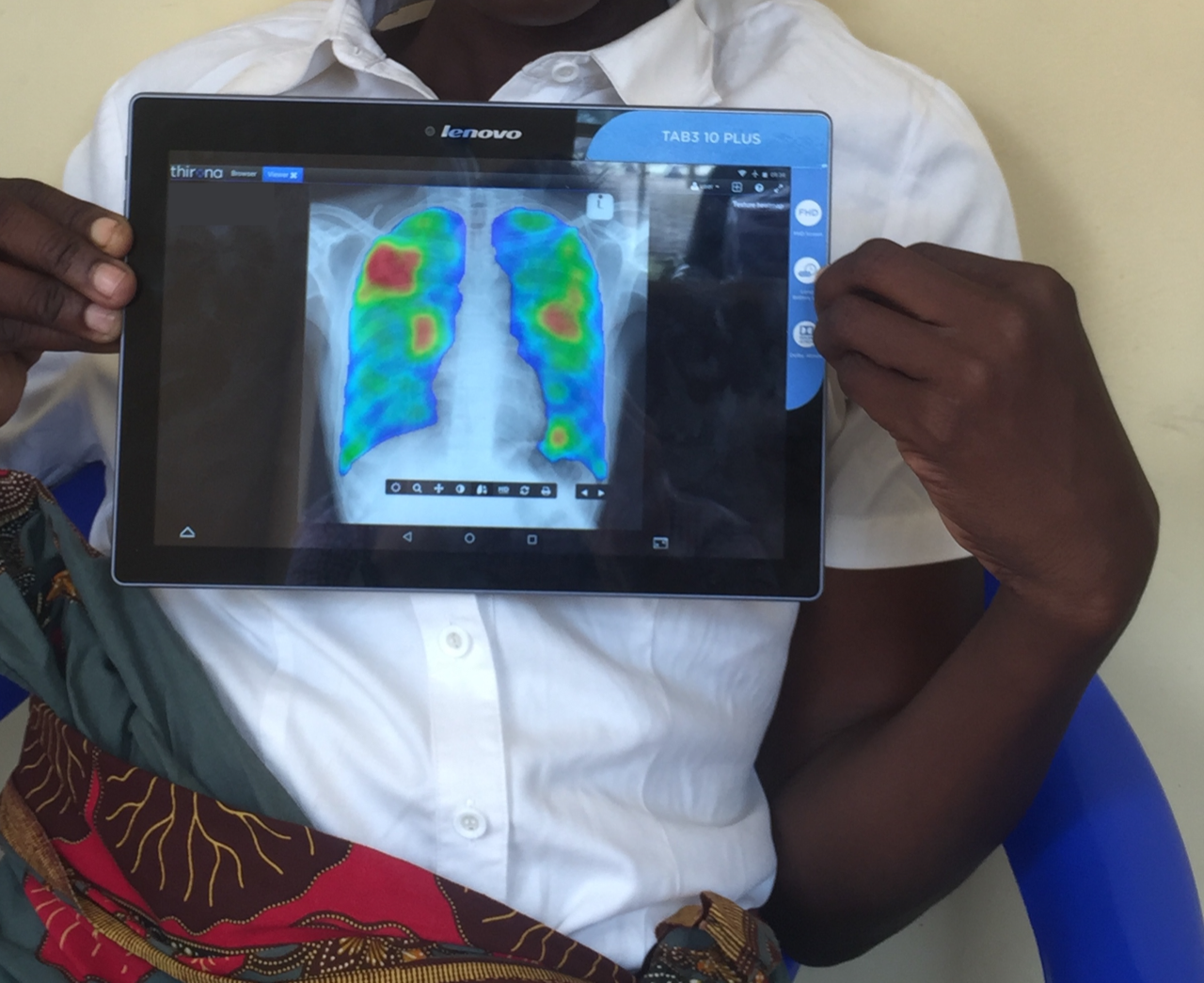
Targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) is a World Health Organization-recommended diagnostic technology that analyzes targeted sections of a bacteria or virus. In global health, tNGS can be used to quickly identify a range of diseases and is particularly useful against TB, which sees high rates of gene mutations that can render treatment regimens ineffective. Because tNGS can quickly detect resistance profiles, it can be used to provide health care providers with more complete information so they can tailor treatments for patients.
The diagnostic technology has applications beyond TB and is a valuable tool that can detect a variety of pathogens and, when needed, their susceptibility to medications, including HIV, hepatitis and COVID-19. The COVID-19 pandemic drove broad uptake of sequencing platforms, meaning that the equipment needed for tNGS is now far more widely available than it was pre-pandemic, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
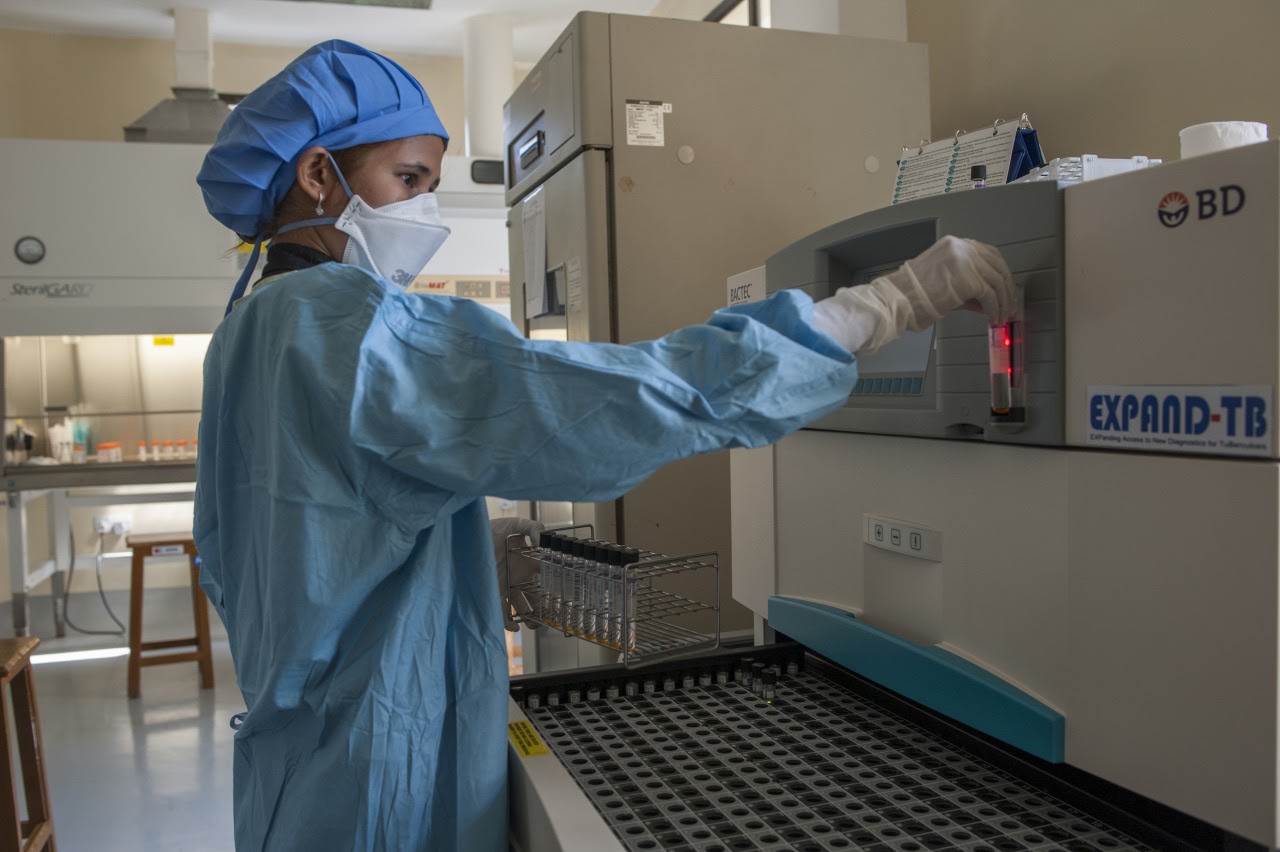
Because TB is so complex to treat, requiring a combination of several antibiotics at once, and because drug resistance is becoming increasingly common, it is critical that health care providers can identify the drugs that are most likely to be effective. tNGS can provide comprehensive drug resistance profiling for both first- and second-line TB drugs, enabling more tailored treatments. Importantly, tNGS is the only testing method that can quickly identify resistance to bedaquiline, a key drug that is used in newer, shorter drug-resistant TB treatments.
Though tNGS is not the fastest diagnostic method, it is significantly more sensitive and adaptable than other diagnostic methods and provides faster results than most other options. TNGS platforms can be regularly updated with evolving mutation profiles, which is important in staying ahead of drug resistance.
Together with FIND through our Seq&Treat project, we have demonstrated how tNGS can be used for TB drug resistance testing, informing the World Health Organization’s (WHO) recommendation for broader use of this technology. Seq&Treat developed a TB sequencing portal, which serves as the knowledge base to understand the association between mutations in the genes and resistance to TB medicines. The portal helps ensure that countries have the latest data on TB drug resistance and that emerging resistance profiles can be quickly added to tNGS platforms.
Though tNGS platforms can be expensive and more complex to implement, their use in identifying and monitoring COVID-19 triggered rapid uptake of the technology around the world, which now gives low- and middle-income countries the opportunity to leverage those infrastructure improvements for the TB response.